Cataracts are a frequent age-related disorder that impairs the clarity of the lens of the eye. Senile immature cataracts are very common in the elderly population. Cataracts build gradually and can have a major influence on visual quality, reducing one’s ability to conduct daily duties. This article will look at the nature of senile immature cataracts, how they affect vision, and how to manage and treat the issue.
Understanding Senile Immature Cataracts
What Are Cataracts?
Cataracts are the clouding of the eye’s natural lens, which is located behind the iris and pupil. This clouding can disrupt the flow of light through the lens, resulting in blurred or decreased vision. Cataracts can appear in one or both eyes, but they do not spread from one to the other.
What Are Senile Immature Cataracts?
Senile immature cataracts are a form of age-related cataract that has not fully matured or become “mature.” This indicates that the lens’s clouding is still in its early stages, enabling some light to flow through, albeit with difficulty. As the cataracts grow, they might get denser and more opaque, severely compromising eyesight.
Causes and Risk Factors
Senile immature cataracts are primarily caused by aging. As humans age, the proteins in the lens of the eye tend to degrade and clump together, resulting in foggy patches. Other contributing causes to the development of cataracts include:
- Genetics: A family history of cataracts can raise your chances of developing them.
- UV Exposure: Prolonged exposure to UV radiation can harm the proteins in the lens.
- Smoking: Smoking increases the risk of developing cataracts.
- Diabetes: Diabetics are more likely to get cataracts.
- drugs: Long-term use of certain drugs, such as corticosteroids, might lead to cataract formation.
- Eye Injuries: Trauma to the eye might result in cataracts.
Impact on Vision Quality
Gradual Vision Deterioration
Senile immature cataracts develop slowly, and their impact on visual quality is usually gradual. Initially, people may not detect substantial changes in their vision. However, as cataracts advance, they may cause:
- Your vision may get increasingly blurry, making it difficult to perceive minute details.
- Individuals may be more sensitive to light, glare, and halos around lights, particularly at night.
- Colors may appear less bright and washed-out.
- Some people may suffer double vision in one eye.
- Seeing in low light circumstances can be difficult, making night driving much more difficult.
Daily Life Impact
A slow decline in visual quality can have a significant influence on daily life. Clear-vision tasks, such as reading, driving, and recognizing faces, can become more challenging. This can result in loss of independence and a lower quality of life. Furthermore, increased glare and trouble with night vision might pose safety issues, especially for older persons who are already at a higher risk of falling and being injured.
To gain more information, here is our doctor from Dr Agarwals eye hospital explaining everything about cataracts.
Diagnosis and Monitoring
Eye Exams
Regular eye exams are essential for the early detection and monitoring of senile immature cataracts. During an eye exam, an eye care expert will do various tests, including:
- Visual acuity test: Determines how well you can see at different distances.
- Slit-Lamp Examination: This allows the doctor to examine the structures in the front of the eye, including the lens.
- A retinal exam involves dilation of the pupils in order to inspect the retina and the back of the eye.
- Tonometry measures the pressure inside the eye.
Monitoring Progression
Individuals diagnosed with senile immature cataracts require regular monitoring to track the condition’s progression. This aids in selecting the optimal time for prospective surgical intervention, if required.
Management and Treatment
Non-Surgical Approaches
In the early stages of senile immature cataracts, non-surgical methods can help manage symptoms and maintain visual quality:
- Updating prescription glasses might help increase visual clarity.
- Special lenses can reduce glare while increasing comfort.
- Magnifying glasses or gadgets can be useful for close-up tasks such as reading.
- Increasing the quantity of light in living areas can boost visibility.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Certain lifestyle changes can help manage the symptoms of cataracts:
- UV Protection: Wearing UV-blocking sunglasses can help reduce the progression of cataracts.
- Healthy Diet: A diet high in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals can benefit eye health.
- Smoking cessation: Quitting smoking can lower the risk of cataract advancement.
- Managing Health Conditions: Keeping diabetes under control can assist to slow cataract development.
Surgical Intervention
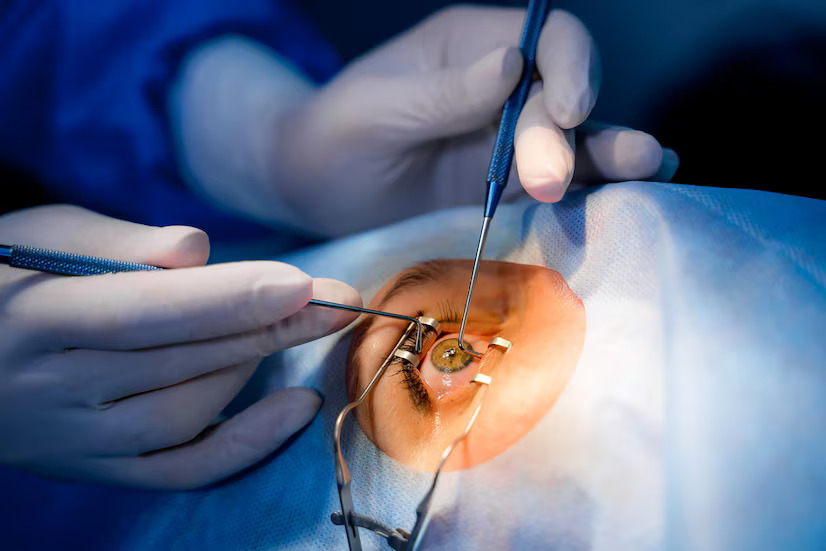
When cataracts severely impair eyesight and reduce quality of life, surgical intervention may be required. Cataract surgery is one of the most popular and successful surgical treatments performed worldwide. The operation entails removing the clouded lens and replacing it with an artificial intraocular lens.
Types of Cataract Surgery
- The most common technique is phacoemulsification, which involves breaking up the clouded lens with an ultrasonic device before removing it through a small incision.
- Extracapsular Cataract Extraction (ECCE) involves removing the clouded lens in one piece via a bigger incision. This procedure is less usually performed, however it may be required for highly advanced cataracts.
Post-Surgery Care
Patients often report a considerable improvement in visual quality following cataract surgery. Post-surgery care involves:
- Schedule regular check-ups to evaluate healing and ensure optimal vision.
- Wearing protective eyewear can help prevent harm throughout the healing process.
- Applying prescription eye drops to prevent infection and irritation.
Conclusion
Senile immature cataracts may significantly reduce vision quality, affecting everyday life and general well-being. While the illness worsens gradually, regular eye exams and early discovery are critical for controlling symptoms and deciding the best time for surgical repair. Individuals can improve their quality of life and retain superior eyesight by making lifestyle changes and taking proactive efforts to safeguard their eyes. If you feel you or your loved one is getting cataracts, speak with an eye care specialist to determine the best course of action.