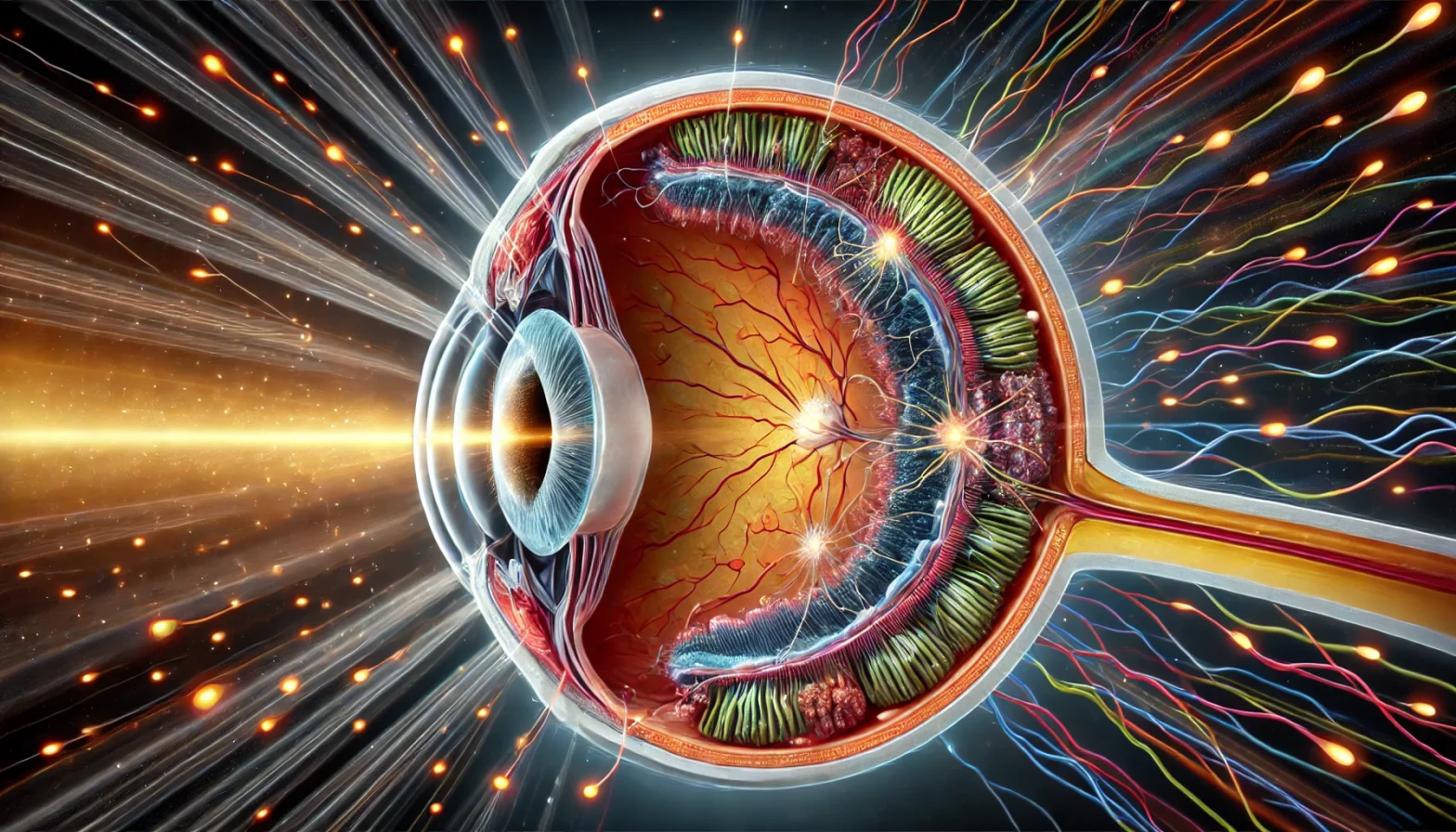
The retina refers to the eye’s inner lining, a part of the eye that contains light-sensitive tissues. Its major role is to help in vision generation by sending light signals to the brain. In some patients, the retinal tissue start thinning and breaking down overtime at certain locations. This retinal break is a tiny hole that usually develops in the peripheral part of the retina. In rare cases, the vitreous gel (gel present in the eyes) can cause a retinal tear formation when it detaches from its attachments on the retina.
Formation of retinal tears and holes can predispose to retinal detachment if and when the fluid inside the cavity o the eye passes through the hole under the retina and ends up detaching it in the process. The retinal separation or retinal detachment may not cause vision loss immediately, but eventually. The initial symptoms of retinal detachment can be floaters and flashes of light around the eyes. Some retinal detachments don’t need treatment, but most require treatment to prevent complete blindness. If you are experiencing floaters (black, enlarged spots) in your vision, it is a good idea to get your retinal evaluation done by a good retina eye doctor.
What are the treatment options for a retinal break?
The best method to prevent retinal detachment is to seal the tiny holes in the retina. Your retina specialist will first examine your eye condition and then suggest one of the following retina treatments:
Laser Photocoagulation:
In this procedure, an ophthalmologist will put eye drops to dilate your pupil. The eye surgeon will apply anesthetic drops in the eyes for a painless treatment. Then the surgeon will use the laser machine and with the help of the special retina laser seal the retina around the retinal holes and tears. The laser photocoagulation is a painless and quick procedure and is mostly performed on an outpatient basis. For the first few hours post-treatment, you may experience blurred vision.
Cryopexy:
This procedure uses a cryoprobe to freeze the tissues around the retinal tear. Cryopexy is performed under local anesthesia for patient comfort during the treatment. The damaged hole is secured to the inside of the eyeball to seal the hole. . After the treatment is complete, your eyes may appear red for a few days. Therefore, you must follow your eye doctor’s advice and take prescribed medicines for a speedy recovery.
Takeaway
Although laser eye treatment is often painless, some patients complain of experiencing a mild “electric shock-like” feeling during the process. The recovery ratio is excellent for laser/Cryopexy procedure, as it doesn’t involve incisions or cuts around the retina. There is no risk of retinal infection, and the patient heals very quickly.