What are Eye Exercises?
Eye exercises is a general term given to the activities performed by the eye wherein the patient is asked to see specific patterns / focus at a particular distance / perform activities for specific duration according to a treatment plan.
Below eye exercises may be advised to patients to:
- Relieve symptoms of eye strain
- Improve ability to see
- Decrease complaints of double vision
- Decrease laziness of the eye
- Improve ability to focus on objects
They are generally part of vision therapy, binocular vision clinic, squint clinic or eye exercise clinic.
Why are Eye Exercises required?
Physiotherapy is generally advised to strengthen particular muscles of the body and enable better functioning. Similarly the eye also has muscles and exercises are advised to improve the functioning of the eye.
The eye has 2 types of muscles:
- External muscles: these muscles help the eye to move in a direction. They ensure that both the eyes move in synchrony. Sometimes the balance between the two eyes may be affected and suitable eye exercises can help the individual. In severe cases surgical or other treatment may be required.
- Internal muscles: these muscles help the eye to focus at a particular distance or object. If there is difficulty in focusing, advice is given to enable strengthening of the muscles involved. This would improve the ability of the eye to focus and see clearly.
How is the problem diagnosed?
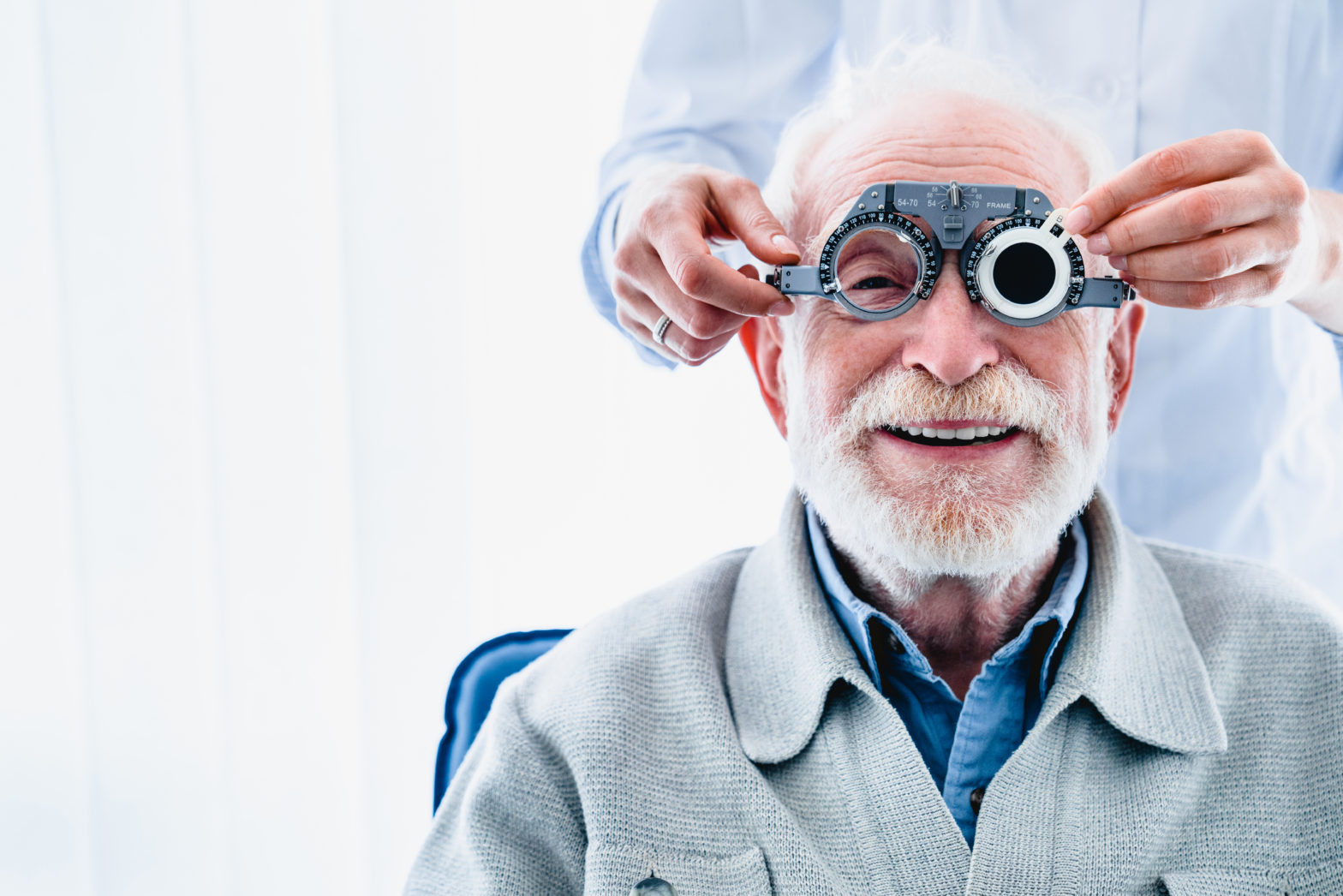
- A comprehensive eye test is required to diagnose the problem.
- Detailed history is required to understand the cause of the problem and the type of the problem. Profession and symptoms provide inputs on the type of the problem.
- Based on the history and symptoms, the practitioner uses different tools like prisms, binocular string and flippers to diagnose the problem.
What are the common symptoms in patients with weak muscles?
- Diplopia: the patient may be seeing two images occasionally or the problem may be present constantly. Sometimes patients may be able to control with effort the diplopia.
- Eye Strain: this is a common symptom in patients. The problem may continue to present even after change of glasses or wearing of glasses.
- Headache: individuals may complain of more frontal headache or general heaviness & tiredness
- Difficulty in reading: generally patients experience difficulty in doing near work for a longer period of time.
The problems are generally found in individuals below 38 years
Individuals specializing in diagnosis and treatment of the eye muscle problems, are called Orthoptists. This is part of the curriculum of optometrists.
What is the cause of the problem?
- General body weakness: this can lead to problems of strain. This may get resolved once the general weakness is cured
- Different power between the eyes: the spectacle power can be vastly different between the two eyes and can contribute to eye strain
- Difference in vision: if vision is lower in one of the eyes, then it can contribute to mis – alignment (squint) and imbalance of vision
Additionally, computer work and prolonged near work can exacerbate an existing problem.
There are many more reasons that can lead to the problems and only a comprehensive assessment can lead to correct diagnosis. Sometimes the correct cause of the problem may not be known and the treatment would focus on providing symptomatic relief.
What type of eye exercise is required?
The eye exercises would depend on the cause of the problem and understanding of the muscles involved. The therapy can broadly be classified into:
- Computer-based therapies: these are convenient for the patient as they can be done at the convenience of the patient at their home
- Machine therapy: the patient would have to come to the concerned centre based on the clinician’s advise and follow the routine
- Activity-based therapy: under this the individual would be required to perform particular visual activities for said duration
- Prisms: prismatic power may be incorporated to relieve the strain or as a temporary measure to strengthen the muscles
The duration and type of eye exercises would depend on the extent of the problem. Follow – up is essential to understand the progress. Sometimes an exercise can be advised to sustain the benefits gained.
The eye exercises do not help in removing spectacle power that the eyes may require to see, but they can help in better tolerating the strain the individual will face while seeing.