What is Keratoconus?
Keratoconus is a progressive eye condition that causes the cornea, the clear, dome-shaped front surface of the eye, to thin and bulge outward into a cone shape. This irregular shape distorts vision, leading to symptoms such as blurred vision, glare, and sensitivity to light. The condition often starts in adolescence or early adulthood and may gradually worsen over time. In its advanced stages, keratoconus can significantly impact daily activities, making it difficult to read, drive, or see clearly without corrective lenses or surgical intervention.
Doctor Speaks: All about Keratoconus
What are the Symptoms of Keratoconus?
Keratoconus symptoms vary depending on the severity of the condition. The most common symptoms include:
-
Blurred vision:
Blurred vision is one of the earliest and most noticeable signs of keratoconus. As the cornea changes shape, light entering the eye gets scattered, causing objects to appear unclear or distorted.
-
Ghosting of images:
Many individuals with keratoconus experience ghosting or double vision, where images appear duplicated or overlapped. This can occur even when wearing glasses or contact lenses, making it challenging to achieve sharp vis
-
Distorted vision
Due to the irregular shape of the cornea, keratoconus often causes straight lines and objects to appear wavy or bent. This visual distortion makes reading and other close-up tasks difficult.
-
Sensitivity to light
Increased sensitivity to light (photophobia) is common in people with keratoconus. Bright lights, such as headlights and sunlight, may cause discomfort and make it harder to see clearly, especially at night.
-
Glare
Glare and halos around light sources, especially at night, are frequent complaints among those with keratoconus. This makes activities like night driving particularly challenging.
-
Frequent change in glass prescriptions
As keratoconus progresses, individuals often find that their eyeglass prescription changes frequently. This is due to the cornea’s continuous reshaping, which alters how light is focused onto the retina.
Causes of Keratoconus
The exact cause of keratoconus is not fully understood, but several factors are believed to contribute to its development:
-
Genetics: A family history of keratoconus increases the likelihood of developing the condition.
-
Excessive Eye Rubbing: Frequent or vigorous rubbing of the eyes may weaken the cornea over time, contributing to its thinning and bulging.
-
Underlying Medical Conditions: Conditions such as asthma, Down syndrome, and connective tissue disorders are associated with a higher risk of keratoconus.
- Oxidative Stress: Imbalance in the eye’s natural defense mechanism against oxidative stress may weaken the corneal structure.
Keratoconus Treatment and Management
The treatment options for keratoconus depend on the severity of the condition. Early-stage keratoconus can often be managed with corrective lenses, while advanced cases may require medical or surgical intervention.
-
Eyeglasses and Contact Lenses
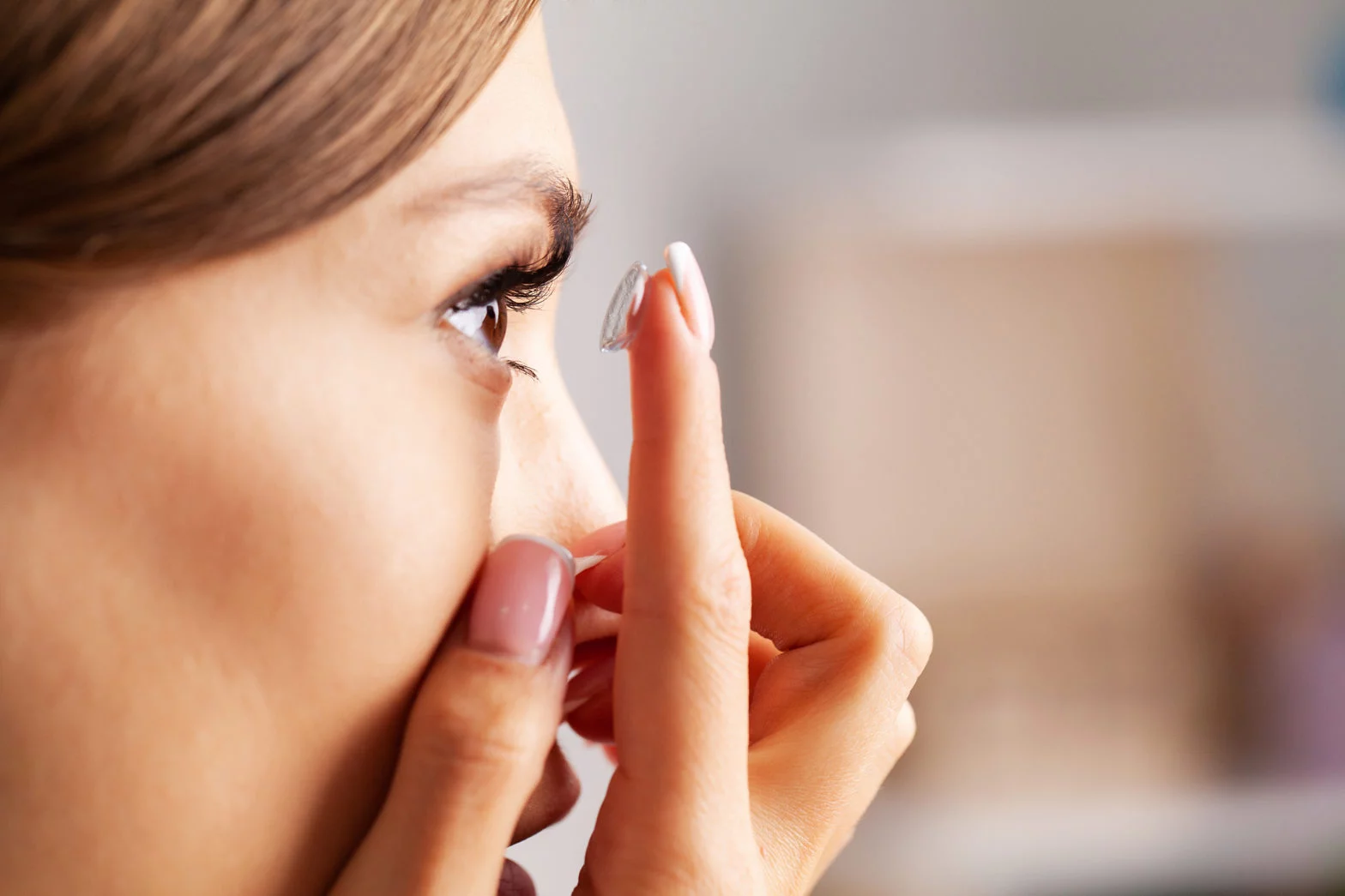
In the early stages, eyeglasses or soft contact lenses can help correct vision by compensating for mild corneal irregularities. As the condition progresses, specialized lenses such as rigid gas permeable (RGP) lenses or scleral lenses are often needed.
-
Corneal Cross-Linking (CXL)
Corneal cross-linking is a minimally invasive procedure designed to strengthen the cornea and slow the progression of keratoconus. The treatment involves applying riboflavin (vitamin B2) drops to the eye and activating them with ultraviolet (UV) light.
-
Intacs (Corneal Implants)
Intacs are small, arc-shaped inserts that are surgically placed in the cornea to flatten its shape and improve vision. This procedure is often recommended for moderate cases of keratoconus.
-
Keratoconus Surgery (Corneal Transplantation)
In advanced cases where vision cannot be corrected with lenses or less invasive treatments, a corneal transplant (keratoplasty) may be necessary. During this procedure, the damaged cornea is replaced with a healthy donor cornea.
Keratoconus Self-Care Tips
Managing keratoconus involves lifestyle changes and self-care strategies to slow its progression and improve visual comfort:
-
Avoid excessive eye rubbing.
-
Wear UV-protective sunglasses to shield your eyes from harmful rays.
-
Use lubricating eye drops to prevent dryness and irritation.
-
Follow up regularly with an eye specialist to monitor changes.
-
Maintain a healthy diet rich in antioxidants to support eye health.
Types of Keratoconus
Keratoconus is classified into different types based on the severity and shape of the corneal deformation:
-
Nipple Cone:
A small and centrally located steep cone.
-
Oval Cone:
A larger cone that is displaced towards the lower part of the cornea.
-
Globular Cone:
A large, round cone affecting a significant portion of the cornea.
Risk Factors of Keratoconus
Several risk factors increase the likelihood of developing keratoconus, including:
-
Genetic Predisposition:
A family history of keratoconus raises the risk of developing the condition.
-
Chronic Eye Rubbing:
Persistent eye rubbing, especially in individuals with allergies, may contribute to corneal thinning.
-
Environmental Factors:
Exposure to UV rays and oxidative stress can accelerate corneal degeneration.
-
Medical Conditions:
Conditions such as Down syndrome, Marfan syndrome, and Ehlers-Danlos syndrome are linked to keratoconus.
Diagnosis of Keratoconus: Tests and Procedures
Eye specialists use several diagnostic tests to detect and assess keratoconus:
-
Corneal Topography: A detailed imaging test that maps the shape of the cornea to detect abnormalities.
-
Pachymetry: Measures the thickness of the cornea to identify thinning areas.
-
Slit Lamp Examination: A detailed eye exam that helps assess corneal health and detect early signs of keratoconus.
Treatment and Management Options for Keratoconus
The treatment options for keratoconus depend on the severity of the condition. Early-stage keratoconus can often be managed with corrective lenses, while advanced cases may require medical or surgical intervention.
-
Eyeglasses and Contact Lenses
In the early stages, eyeglasses or soft contact lenses can help correct vision by compensating for mild corneal irregularities. As the condition progresses, specialized lenses such as rigid gas permeable (RGP) lenses or scleral lenses are often needed.
-
Corneal Cross-Linking (CXL)
Corneal cross-linking is a minimally invasive procedure designed to strengthen the cornea and slow the progression of keratoconus. The treatment involves applying riboflavin (vitamin B2) drops to the eye and activating them with ultraviolet (UV) light.
-
Intacs (Corneal Implants)
Intacs are small, arc-shaped inserts that are surgically placed in the cornea to flatten its shape and improve vision. This procedure is often recommended for moderate cases of keratoconus.
-
Keratoconus Surgery (Corneal Transplantation)
In advanced cases where vision cannot be corrected with lenses or less invasive treatments, a corneal transplant (keratoplasty) may be necessary. During this procedure, the damaged cornea is replaced with a healthy donor cornea.
Precautions After C3R Surgery for Keratoconus
After undergoing corneal cross-linking (C3R) surgery, it is essential to follow specific precautions to ensure proper healing:
-
Avoid Eye Rubbing:
Rubbing the eyes can interfere with the healing process and increase the risk of complications.
-
Use Prescribed Eye Drops:
Follow the doctor’s instructions for medicated eye drops to prevent infection and inflammation.
-
Protect Your Eyes
Wear sunglasses to shield your eyes from UV exposure and reduce light sensitivity.
-
Limit Screen Time
Reduce strain on your eyes by minimizing screen usage and taking frequent breaks.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Keratoconus
What are the 4 stages of keratoconus?
The four stages of keratoconus are Mild (Stage 1) – slight corneal thinning and blurred vision, Moderate (Stage 2) – increased distortion, need for rigid contact lenses, Advanced (Stage 3) – significant corneal bulging, severe vision impairment, and Severe (Stage 4) – extreme thinning, corneal scarring, and possible need for a corneal transplant.
Can keratoconus cause blindness?
Keratoconus does not directly cause total blindness, but it can severely impair vision if left untreated. In advanced stages, corneal scarring and extreme distortion can make vision extremely poor, requiring treatments like corneal cross-linking, specialty lenses, or even a corneal transplant to restore functional sight.
Is Keratoconus Curable or Can It Be Managed?
Keratoconus cannot be cured, but it can be effectively managed with treatments such as glasses, contact lenses, corneal cross-linking (C3R), and, in advanced cases, corneal transplants.
Can Keratoconus Progress After C3R?
In most cases, corneal cross-linking stabilizes keratoconus and prevents further progression. However, in some cases, progression can occur over time, requiring additional interventions.
What are the early signs of keratoconus?
Early signs include blurred or distorted vision, increased sensitivity to light, frequent changes in eyeglass prescriptions, and difficulty seeing at night.
What causes corneal thinning in keratoconus?
Corneal thinning in keratoconus is caused by a combination of genetic, environmental, and biochemical factors that weaken the corneal structure over time.
Do not ignore eye trouble!
Now you can reach our senior doctors by booking an online video consultation or a hospital appointment
Book an appointment now