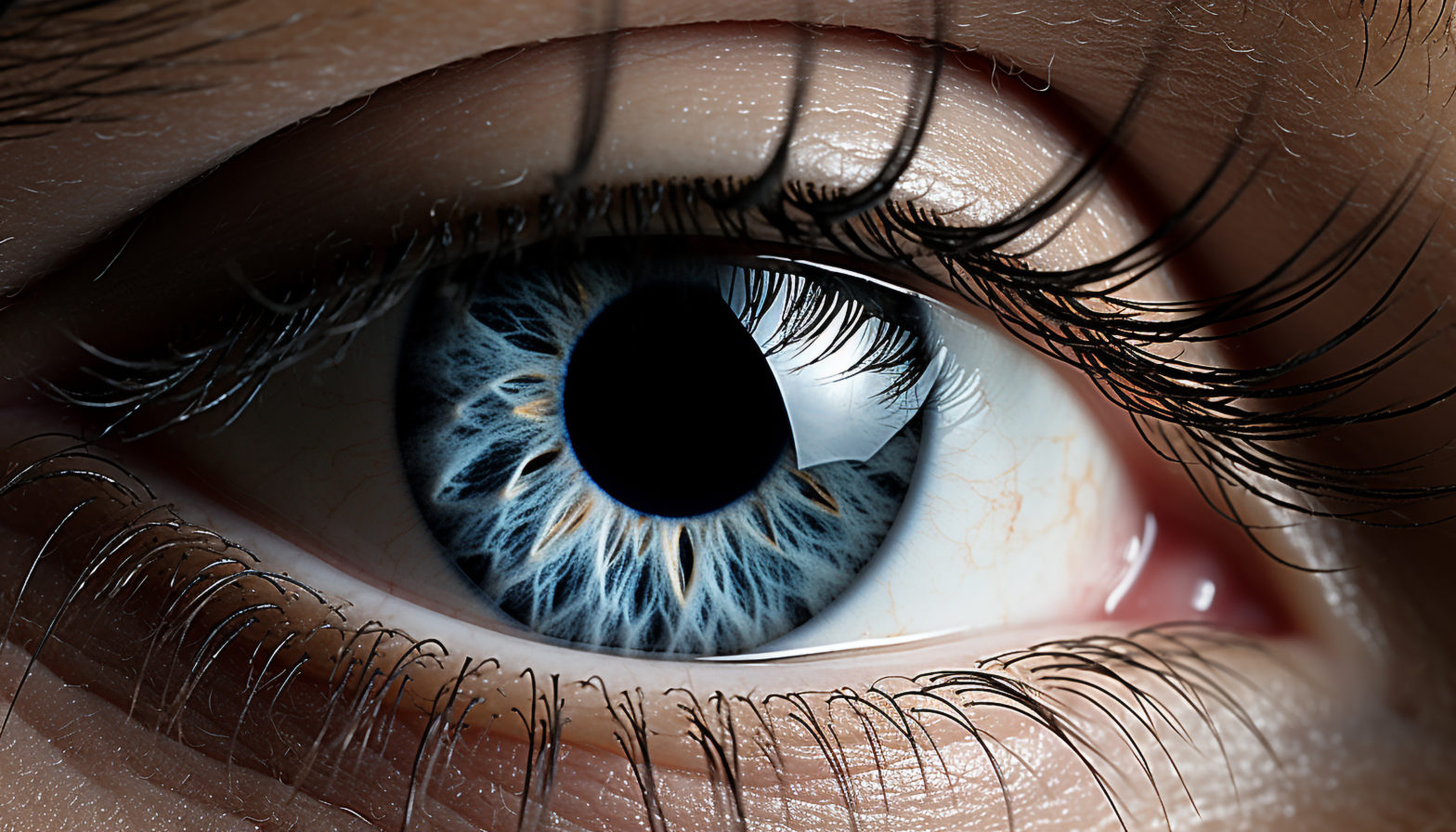
What is Keratoconus?
Keratoconus is a condition in which the normally round cornea becomes thin and develops a cone-like bulge.
What are the symptoms of Keratoconus?
- Blurred vision
- Double vision
- Light Sensitivity
- Multiple images
- Eye strain
- ‘Ghost images’-Appearance like several images when looking at one object
How is Keratoconus diagnosed?
Keratoconus is usually diagnosed on routine eye examination. A slit lamp eye examination can be used for the diagnosis of Keratoconus. Most of the time corneal topography is required for the diagnosis of Keratoconus. Other than that Keratometry, Pachymetry and computerized corneal mapping is helpful for determining the shape of the cornea.
Whether dilatation is required for the eye examination in Keratoconus?
Your eyes will be dilated as a part of the examination to view the vitreous and retina in the back part of the eye. The eye dilatation makes the vision blurry and the eyes will be more sensitive to light for few hours. It is recommended to have someone drive you back home.
- Slit lamp Examination:- In this test a vertical beam light is focused on the surface of the eye. It helps to evaluate the shape of the cornea and eye diseases.
- Corneal topography:-It is a computerized instrument that makes three-dimensional maps of the cornea. It helps in the diagnosis of Keratoconus differentiating from other eye diseases.
- Pachymetry:- It is a medical device which helps to measure the thickness of the eye’s cornea. It is necessary for the doctor to know the corneal thinning and/or swelling in the cornea.
- Keratometry:- It is a test to measure the reflection and basic shape of the cornea. It helps in assessing the extent and axis of astigmatism.
- Computerized corneal mapping: – It is a special photographic test to record the images of the cornea and create a detailed map of the cornea’s surface. This test helps to measure the thickness of the cornea.